Quantum Mechanical Model of single Carbon Atom.
MODELS PRINTED IN COLOR ON GLOSSY,
110# CARD-STOCK PAPER READY TO BE
CUT OUT BY STUDENTS
Tools needed for cutting out and assembling Carbon atom model.
- Scissors.
- 1/4” single-hole punch.
- Cellophane tape for repairs.
Useful for: HS-PS1-1. Use periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of elements based on the patterns of elections in the outermost energy.
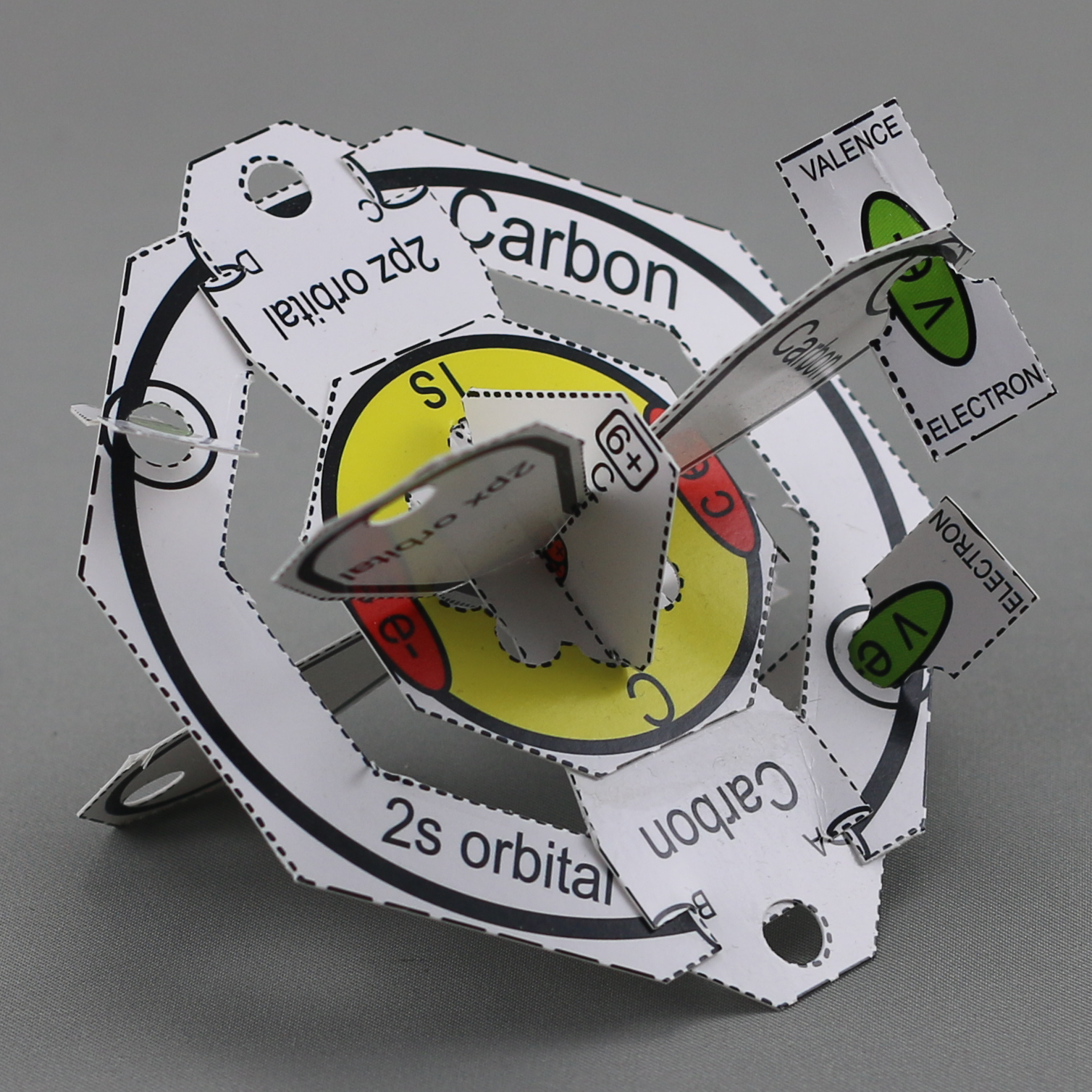
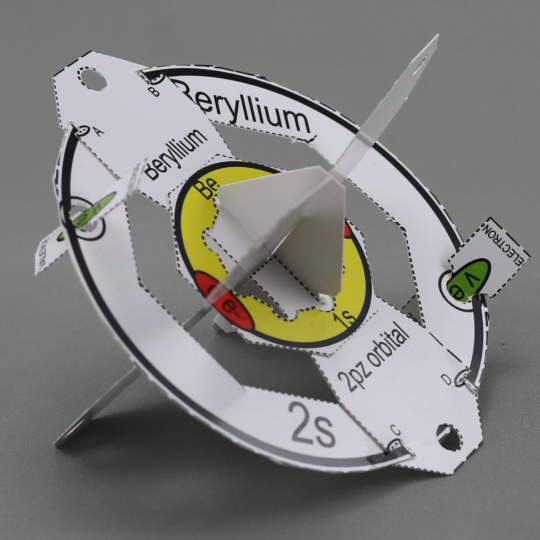
- The carbon model is a physical representation of the mathematical equations that define the quantum mechanical model of carbon.
- The model shows the first and second energy levels (shells), sub-levels, and the orientations of orbitals within them.
- The first energy level displays two core electrons as red ovals. (The color red refers to cars being stopped and not able to go at traffic lights. Therefore core electrons cannot leave the atom as indicated by red.)
- The outermost energy level (second energy level for carbon) has four valence electrons with a green oval. (Cars can go on green at traffic lights. Valence electrons can go, or leave the atom as indicated by green.)
- This model can be dismantled so that the orbitals can be placed on an orbital diagram which is available from Quanta to Galaxies. The symbol for an electron, core or valence, in an orbital diagram is an arrow. The electrons in the model are not real, but they are a step closer to reality than written symbols and help to understand what the arrows and other symbols in orbital diagrams and electron configurations represent.
- Quantum mechanics requires that all atoms are both neutral and stable. Neutrality is accomplished with number of electrons being equal to number of protons. Stability is accomplished when the outermost energy level is filled with electrons, or totally empty. This means two electrons for hydrogen and helium and eight electrons for all other atoms (octet rule).
- The carbon model displays six protons in the nucleus and six electrons in the first and second energy levels. Therefore, it is neutral. (Since neutron numbers vary they are not shown in these models. There are lessons available specifically about isotopes! that deal with variable neutron numbers.)
- Carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost energy level and four empty holes that could hold electrons. Thus carbon is not stable as presented by this model. If the four valence electrons remain and the four empty holes are filled with electrons shared from other atoms resulting in the formation of a molecule, the outermost energy level will be filled. This leaves the new structure stable and if the carbon is now part of a molecule the net charge is zero and neutrality is accomplished also.
This carbon atom model can be used with other atom models from periods 1, 2, 3, and 4 to analyze periodic trends.
Also useful for: PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter
As noted already, the model provides a three dimensional display of the structure of the carbon atom which is relevant to NGSS standard PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter and provides the following:
- A great hands-on manipulative for classroom activities that can engage the student in active learning with more material retained.
- Hands-on learning environment that develops critical thinking.
- Use of materials and equipment.
- A model that is a step or two closer to reality than printed text or drawings.
- A lesson that sometimes is just more fun.
Some teachers have already reported to us that the models have stimulated conversations among students relevant to the proposed lesson before the teacher even begins to interact with the students.
Completion of the physical model has been reported to give many students a sense of pride in being able to do more than read and respond. Parents have reported that some of the students have kept and displayed their model for as many as ten years after graduation.
And useful for: MS-PS1-1. Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structure.
Carbon does not usually lose four electrons of gain four electrons. It will generally share electrons with other atoms. The carbon model can be attached to other atoms with the valence electrons to form neutral molecules. When carbon has four hydrogen atoms attached to it the result is a neutral methane molecule. This model can be assembled from a hybridized carbon atom model and four “folding” hydrogen atom models.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.